Governance
The Ontario Securities Commission Charter of Governance was established to promote transparent, accountable and informed governance. The Ontario Securities Commission is committed to excellence in our governance practices. That commitment is supported by clear roles and responsibilities, effective processes and reporting, and extensive strategic planning and stakeholder engagement.
We follow the best practices of corporate governance for public companies, where appropriate for a regulator. The OSC aims to continuously advance and innovate its governance framework.
Board of Directors
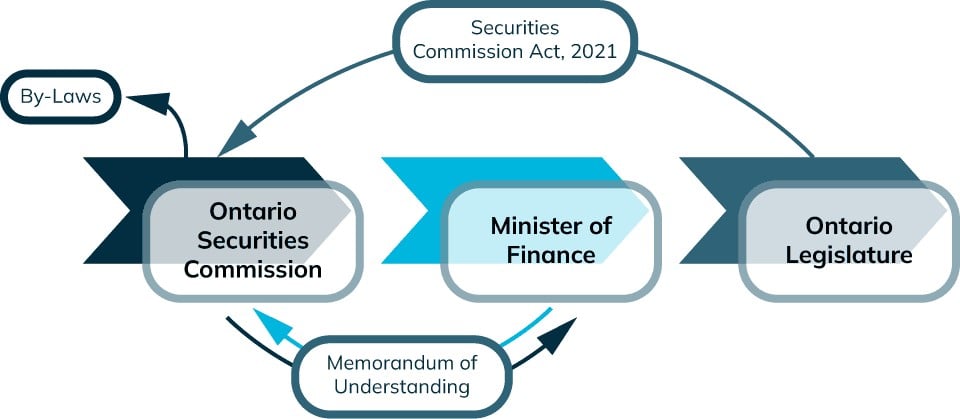
The OSC may have a maximum of twelve Board Directors. The Securities Commission Act, 2021, together with By-law No. 1, provide that the Board of Directors be composed of at least three and not more than eleven individuals appointed by the Lieutenant Governor in Council, plus the full-time Chief Executive Officer. The appointee Board Directors are independent of management and are appointed by the Lieutenant Governor in Council on the recommendation of the Minister of Finance. The Chair of the Commission is designated by the Lieutenant Governor in Council from among the independent Board Directors.

Appointments and reappointments are made in accordance with the Agencies and Appointments Directive, the Memorandum of Understanding, and the procedures of the Public Appointments Secretariat of the Government of Ontario. These government appointments respect the needs of the entity to which they have been appointed, but also reflect the diversity of the people in Ontario and the need to deliver services in a professional, ethical and competent manner.
Our Ontario Securities Commission Charter of Governance provides additional information on Board Director terms, orientation and continuing education, remuneration and attributes.
Board roles and responsibilities
The Board oversees adherence to the principles established by the Government of Ontario, the Memorandum of Understanding, the Public Service of Ontario Act, 2006 and the Ontario Securities Commission Code of Conduct relating to ethical behaviour, accountability, excellence in management, wise use of public funds, high-quality service to the public and fairness in the marketplace.
Regulatory responsibilities
The OSC regulates Ontario’s capital markets by making rules that have the force of law and by adopting policies that influence the behaviour of capital markets participants. The OSC exercises its regulatory oversight function through the administration and enforcement of Ontario’s Securities Act and Commodity Futures Act and administration of certain provisions of Ontario’s Business Corporations Act.
The Board holds strategic planning and priority setting meetings with management to determine the organization’s Statement of Priorities and Business Plan. The Board also holds regulatory meetings, where the Board reviews and approves regulatory initiatives, priorities, policies and rules and discusses general oversight of the capital markets.
Governance responsibilities
The Board is responsible for the overall stewardship of the OSC, including strategic planning and annual budgets, financial review, reporting and disclosure, risk assessment and internal controls and board governance. The Board manages or supervises the management of the Ontario Securities Commission’s affairs, other than matters relating to the Capital Markets Tribunal’s adjudicative functions. It does so through quarterly and special governance meetings of the full Board. The Board has also delegated certain oversight responsibilities to its standing committees while retaining decision-making authority. The Board’s four standing committees are:
- Audit and Finance Committee
- Governance and Nominating Committee
- Human Resources and Compensation Committee
- Risk Committee
Governance authorities and resources